In what’s likely to be the most highly-anticipated event within the cryptocurrency community in 2022, Ethereum’s mainnet is set to merge with the Beacon Chain’s proof-of-stake system.
Dubbed “The Merge,” it will mark the very end of the proof-of-work Ethereum we know today and birth Ethereum 2.0 – the version that will be based on a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm.
We have compiled a very detailed guide on everything you need to know about Ethereum 2.0 that you can check out here. The following focuses on the details surrounding the Merge, some brief technicalities, timelines, and also debunking some of the most coming misconceptions.
What is Fusion?
As mentioned above, “The Merge” is a term, cryptographic slang, if you will, that is used to describe Ethereum’s transition from a proof-of-work consensus algorithm to one that uses proof-of- participation.
The Ethereum Foundation gives an exact definition of the term:
“The Merge represents the joining of the existing execution layer of Ethereum (the mainnet we use today) with its new proof-of-stake consensus layer – the Beacon Chain.”

This is designed to support the energy-intensive mining process while securing the network using staked ETH. This move should provide more security, durability, and scalability to Ethereum’s network.
To shed some more clarity and understanding, let’s dive a bit deeper into the technical side.
The Beacon Chain: The Processing Engine of Ethereum 2.0
The Beacon Chain is the cornerstone of the Ethereum 2.0 architecture. It exists as a separate blockchain from the Ethereum network and operates in parallel. It did not process any transactions on the mainnet, but it reached consensus on its own. This happens by agreeing active validators and their account balances.
The Beacon Chain is secured by a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm, unlike Ethereum’s mainnet, which still runs on proof-of-work. It was created on December 1st, 2020.
Simply put, the Beacon Chain has so far functioned as a de facto testnet for Ethereum 2.0, but all of that is about to change with the merger.
As seen in the above diagram, The Merge represents the moment where the two systems (Ethereum’s current mainnet running on PoW and the Beacon Chain running on PoS) come together. This will see the PoW consensus algorithm replaced by proof-of-stake – permanently.
This has significant implications for the network, but critical considerations include:
- No history will be lost
- Funds are safe
- More ETH mining
When is the Merge?
It’s worth noting that Ethereum 2.0 has been in the making for years, with the exact date of “The Merge” always looking like something set to happen in the not-so-clear distant future.
This all came to an end on July 14, 2022, when a member of the Ethereum Foundation shared a timesheet with what was later described as a “soft” timeline for the merger.

As seen in the image above, The Merge is scheduled to take place on September 19th, 2022, barring any unforeseen events, including “the Goerli Merge not blowing up.”
However, this date is not set in stone and there could be delays in case of complications.
How to Prepare for The Merge?
This is one of the biggest events in the history of the entire cryptocurrency industry, and as such, it is likely that many bad actors will try to exploit it and scam innocent people out of their money.
This is why it is imperative to know that users and holders of ETH have nothing to do with their funds or with their wallets before the merger.
The entire history of Ethereum – dating back to its genesis – will remain unaltered and intact after the transition to PoS. All funds held in a wallet will still be accessible after the Merge, and there is no action required to upgrade on behalf of users and holders.
Nevertheless, the Ethereum ecosystem contains more than users and holders.
- Staking node operators and providers
The most important actions to do if you’re operating a staking node are to first run a consensus layer client and an execution layer. You should authenticate both layers with a shared JWT secret so that they can communicate securely. You should also set a fee recipient address to receive the transaction fee tips you’d get.
- Node operators without validation and infrastructure providers
The key actions here are to install a consensus layer client in addition to the execution layer client. Again, you need to authenticate both clients with a shared JWT secret so they can communicate secretly with each other.
- Smart contract and DApp developers
The Merge will introduce serious structural changes to Ethereum, and developers are encouraged to look at Ethereum Foundation member Tim Beiko’s breakdown of How The Merge Impacts Ethereum’s Application Layer.
Ethereum after the merger
One of the promises of Ethereum 2.0 is that of scaling, and Vitalik Buterin claimed that the network would be able to process 100,000 transactions per second. However, The Merge is only the first stage of five of the protocol’s inbound development.
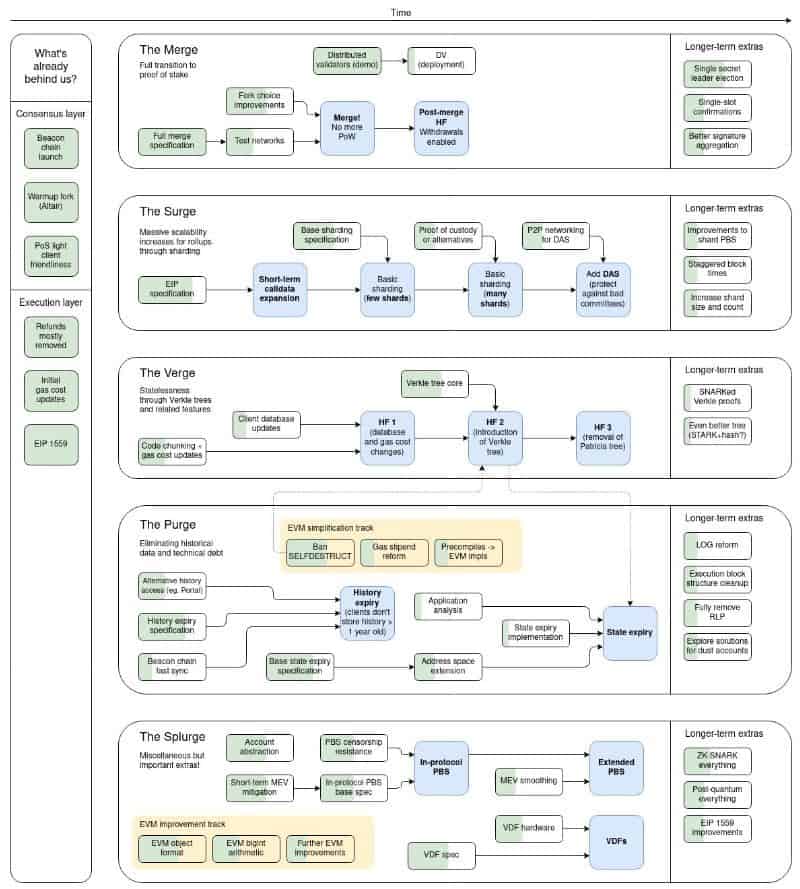
The five stages are as follows:
- The Merge
This is the hereby discussed transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake following the merge of Ethereum’s current mainnet with the Beacon Chain.
- The Surge
This is the phase that will bring sharding to the protocol. It is a scaling solution that would divide the network into separate partitions called “shards”, designed to spread the computational load across the main network.
- The Verge
This phase refers to the introduction of the so-called “verkle trees.” It involves an upgrade to Merkle proofs and is intended to optimize data storage for Ethereum nodes.
- The Splurge
This is the latest upgrade in the pipeline and aims to deliver a series of miscellaneous updates that are done to ensure the overall smooth running of the network.
Top 5 Misconceptions About The Merge
As it is with all highly-anticipated and big events, there are plenty of misconceptions running rampant within the cryptocurrency community. Here are five of the most common one.
It takes 32 ETH to be staked to run a node.
There are two types of nodes on the Ethereum network – one that can offer blocks and one that cannot. Those who are not required to validate ETH do not offer blocks, but they are also integral to network security as they hold all block offerors accountable.
Gas fees will fall down after the Merge.
The Merge will change the overall consensus algorithm and will not expand the network capacity – this is why it won’t result in lower gas fees. However, there are scaling solutions in development that are designed to do just that, most of which are targeted at layer 2s.
The transaction speed will increase significantly.
Mainnet transaction speed will remain relatively the same even after the merger, although there are some slight changes.
The Merge will result in overall network downtime.
The Merge upgrade is designed in a way where there will be zero downtime. The network should keep functioning as intended at all times.
All staked ETH will be withdrawn after the merger.
Validators leaving the network are rate-limited. This is done for security reasons. There are limitations in place that allow approximately 43,200 ETH to exit per day. There are over 13 million ETH in play at the time of this writing.
Conclusion
All in all, The Merge is without a doubt one of the most considerable moments in the history of cryptocurrencies as one of the largest protocols will go through a monumental change. All of this became largely exacerbated now that there’s a timeline in place, albeit “soft.”