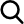LayerZero is a name that has emerged as a market leader in blockchain interoperability.
LayerZero operates by employing two pivotal components, an Oracle and a Relayer. The Oracle plays a key role in sending data across chains, while the Relayer verifies the proof of specific transactions.
Now, let’s unpack the features that make LayerZero stand out:
- Transaction Guarantees: The independence of the Oracle and Relayer is LayerZero’s cornerstone. The confluence of a block header and transaction proof provided by these two independent entities guarantees the validity of a transaction. This is in direct contrast with other “Middle chain” designs of other bridges, which need to rely on their own consensus to secure the assets being transferred.
- Open and Decentralized Network: Any project or team can choose to run their own Relayer or Oracle for the LayerZero network. For instance, Chainlink is an official Oracle provider for LayerZero. This means the cost to attack the protocol is much higher as multiple providers in separate categories need to collude together.
- Risk Sharding & Risk Shielding: LayerZero empowers users to spread the risk by choosing different Oracle/Relayer combinations. Users can even run their own relayers to ensure independence and minimize the possibility of collusion.
- Simple and Effective Design: LayerZero refrains from adding extra mechanisms to its bridging protocol. This means the security of LayerZero is anchored in the native chains of its Endpoints.
Following our exploration of LayerZero’s security features, let’s visualize how a typical transaction works within this system. The image below illustrates the process of a transaction on LayerZero. From initial request to final verification, observe how the Oracle and the Relayer interact to ensure cross-chain functionality

Let’s break down a typical transaction on this network into simpler terms, without delving too deep into the technical nitty-gritty:
- Initiation: A User Application initiates a transaction, sending request details to LayerZero’s Communicator, which packages and forwards the information to the Validator. This essentially notifies the Network of the upcoming cross-chain transaction.
- Notification: The Validator and the Network cooperate to alert the Relayer and the Oracle of their respective tasks – The Relayer needs to fetch the transaction proof, and the Oracle needs to fetch the block header.
- Fetching: The Relayer and the Oracle independently obtain the transaction proof and block header from Chain A, and store this information off-chain.
- Confirmation and Validation: After waiting for block confirmations, the Oracle sends the block header to Chain B’s Network. The Network and the Validator work together to confirm the transaction’s validity by comparing the block header and transaction proof.
- Finalization: Once the transaction is validated, the Communicator on Chain B receives the information and forwards it to the User Application on Chain B, completing the cross-chain transaction.
This brief rundown offers a peek under the hood of LayerZero. It shows how all the parts work together to let a User Application move transaction info from one blockchain to another. It’s proof of LayerZero’s solid design, which is all about making different blockchains talk to each other easily.
Although LayerZero offers a more secure and powerful solution than traditional bridges, it does have 2 main concerns around trust assumptions:
- Dependence on Relayer and Oracle: LayerZero’s security depends on an increasing number of relayers and oracles on the network. Users are reliant on the security of the Relayer and Oracle to pass messages across chains.
- Reliance on Chains’ Security: LayerZero is fundamentally reliant on the native chain of an Endpoint to function correctly. This brings up the question of how LayerZero would handle a major security breach on a native chain, like a 51% attack.
As a testament to its potential, LayerZero has attracted an impressive lineup of backers, including Circle, Sequoia, Andreessen Horowitz, Samsung Next, and Christie’s Inc. The latest funding round saw LayerZero Labs raise $120 million at a staggering $3 billion valuation, three times its valuation in March 2022.
This speaks volumes about the confidence of the market in LayerZero’s vision and its potential to revolutionize the blockchain landscape. For those keeping a close watch on the forefront of blockchain innovation, LayerZero is undeniably something to keep on your radar.